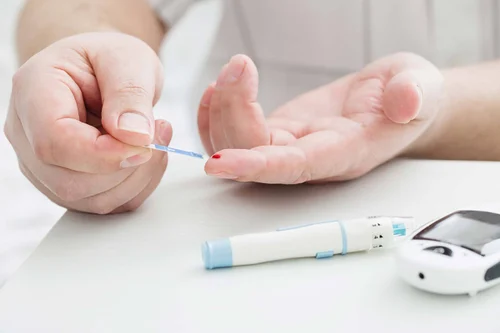
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people globally, with its prevalence increasing rapidly. This metabolic disorder is primarily characterized by high blood glucose levels, which can lead to severe complications if not managed effectively. Diabetes management encompasses a comprehensive approach, integrating lifestyle changes, medication, and regular health monitoring to maintain blood sugar levels within a target range. Effective management not only improves quality of life but also reduces the risk of long-term complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and neuropathy. In this article, we explore essential strategies for managing diabetes, empowering individuals to take control of their health.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Types
To manage diabetes effectively, it is crucial to understand the condition itself. Diabetes is classified into two main types: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to little or no insulin production. This type typically manifests in childhood or adolescence, necessitating lifelong insulin therapy.
Conversely, Type 2 diabetes, the more prevalent form, is often linked to lifestyle factors such as obesity, poor diet, and physical inactivity. In this case, the body becomes resistant to insulin, making it challenging to regulate blood sugar levels. While Type 1 diabetes requires insulin from the outset, Type 2 diabetes can often be managed with lifestyle modifications, oral medications, and, in some cases, insulin therapy as the disease progresses. Understanding these differences is essential for effective diabetes management.
Importance of Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular blood sugar monitoring is the cornerstone of diabetes management. It enables individuals to track how various factors—such as diet, exercise, and medication—affect their blood sugar levels. Most people with diabetes use glucose meters or continuous glucose monitors to keep an eye on their glucose levels throughout the day.
Establishing a personalized monitoring schedule in collaboration with healthcare providers is essential. For some, this may mean checking blood sugar levels multiple times a day, while others may only need to monitor them weekly. Understanding the patterns in blood sugar fluctuations can help individuals make informed decisions about their diet and activity levels.
Healthy Eating Habits
A balanced diet is vital in managing diabetes and maintaining overall health. Focusing on whole, unprocessed foods is crucial for stabilizing blood sugar levels. A well-rounded meal plan should emphasize:
- Fruits and Vegetables: These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber, providing essential nutrients without significantly impacting blood sugar levels. Non-starchy vegetables like spinach, broccoli, and peppers are particularly beneficial.
- Whole Grains: Foods like brown rice, quinoa, and whole grain bread contain fiber, which helps to slow glucose absorption and prevent spikes in blood sugar.
- Lean Proteins: Including sources such as chicken, fish, beans, and legumes is essential for muscle maintenance and satiety.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporating sources of unsaturated fats, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil, can improve heart health and provide sustained energy.
Moreover, portion control is crucial in managing carbohydrate intake. Understanding carbohydrate counting and its impact on blood sugar can significantly enhance diabetes management. Collaborating with a registered dietitian can help tailor meal plans to meet individual needs, preferences, and health goals.
Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity is another key element of effective diabetes management. Exercise not only helps lower blood sugar levels but also improves insulin sensitivity, making it easier for the body to utilize glucose. The American Diabetes Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, which can include activities like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling. Additionally, strength training exercises should be incorporated at least twice a week to build muscle mass, which plays a vital role in glucose metabolism.
Before starting any exercise regimen, individuals should consult their healthcare provider, especially if they have any diabetes-related complications. Simple changes, such as taking the stairs instead of the elevator or going for a walk during breaks, can contribute to overall activity levels and promote better health.
Medication Adherence
For many individuals with diabetes, adherence to prescribed medications is crucial in managing blood sugar levels effectively. This may include insulin for those with Type 1 diabetes and various oral medications for individuals with Type 2 diabetes. Understanding the purpose and potential side effects of medications empowers individuals to take charge of their treatment plan.
Regular consultations with healthcare providers can help patients adjust their medications based on blood sugar readings and lifestyle changes. Involving family members or support networks can also enhance adherence, as they can provide encouragement and reminders to take medications on time.
Conclusion
Effective diabetes management is a multifaceted approach that combines blood sugar monitoring, healthy eating, regular physical activity, and medication adherence. By understanding the nature of diabetes and implementing these strategies, individuals can significantly improve their health and quality of life. Empowerment through education, support, and proactive decision-making is essential in this journey, allowing individuals with diabetes to lead healthier, more fulfilling lives. With the right tools and knowledge, managing diabetes becomes an achievable goal, paving the way for a brighter future.