In an era where fast food and processed snacks are often the norm, the importance of a balanced diet can sometimes be overshadowed. However, the role of nutrition in maintaining and enhancing health cannot be overstated. A well-rounded diet is foundational to overall well-being, influencing everything from energy levels and immune function to mental health and disease prevention.
Understanding Nutritional Balance
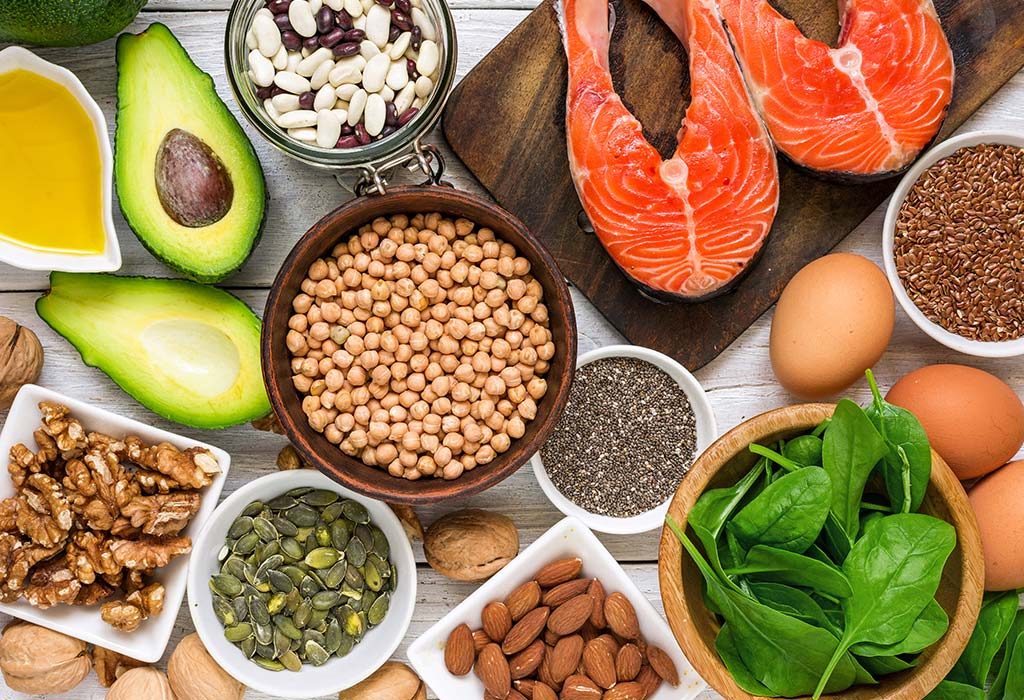
At the heart of a healthy diet is the principle of balance. Nutritional balance involves consuming the right proportions of macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—as well as essential micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals. Each of these components plays a unique role in maintaining bodily functions and promoting health.
- Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source. Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, provide sustained energy and are rich in fiber, which supports digestive health. In contrast, refined carbohydrates, found in sugary snacks and white bread, can lead to energy spikes and crashes, as well as contribute to long-term health issues like obesity and diabetes.
- Proteins are crucial for building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting immune function. High-quality protein sources include lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products, and plant-based options like beans, lentils, and tofu. Ensuring adequate protein intake is particularly important for muscle maintenance and overall bodily repair.
- Fats are essential for absorbing fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) and supporting brain health. However, not all fats are created equal. Unsaturated fats, found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil, are beneficial for heart health. In contrast, trans fats and excessive saturated fats, often present in processed foods, can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and other health issues.
The Role of Micronutrients
Micronutrients, though required in smaller amounts, are just as vital as macronutrients. Vitamins and minerals support a myriad of physiological functions:
- Vitamin C is well-known for its immune-boosting properties. It also aids in collagen production, which is essential for healthy skin and connective tissues.
- Calcium and vitamin D work together to maintain bone health. Calcium supports bone density, while vitamin D enhances calcium absorption in the body. A deficiency in either can lead to bone disorders such as osteoporosis.
- Iron is critical for oxygen transport in the blood. Adequate iron levels are necessary to prevent anemia, which can lead to fatigue and weakened immune function.
The Impact of Nutrition on Mental Health
Emerging research highlights the profound connection between diet and mental health. Nutrient deficiencies and poor dietary choices can contribute to mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. For example, omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish and flaxseeds, are associated with reduced symptoms of depression. B vitamins, particularly folate and vitamin B12, play a role in brain function and mood regulation.
Incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, supports cognitive function and emotional well-being. A balanced diet helps stabilize blood sugar levels, which can prevent mood swings and improve overall mental clarity.
Disease Prevention through Diet
A healthy diet is a powerful tool in disease prevention. Chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers have been linked to poor dietary habits. For instance, diets high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease. Antioxidants, which are abundant in colorful fruits and vegetables, help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body and reduce inflammation.
Reducing the intake of processed foods, high in added sugars and unhealthy fats, can lower the risk of type 2 diabetes. Additionally, dietary patterns such as the Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes whole foods and healthy fats, have been shown to have protective effects against various chronic diseases.
Practical Tips for Achieving Nutritional Balance
Adopting a balanced diet doesn’t have to be complicated. Here are some practical tips to help you get started:
- Plan Your Meals: Creating a weekly meal plan ensures that you incorporate a variety of nutrients into your diet and helps prevent last-minute unhealthy choices.
- Choose Whole Foods: Opt for fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Minimize the consumption of processed and sugary foods.
- Stay Hydrated: Water is essential for every cell in your body. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, and limit sugary and caffeinated beverages.
- Practice Portion Control: Pay attention to portion sizes to avoid overeating. Using smaller plates and bowls can help regulate portion sizes.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how different foods make you feel. Eating mindfully can help you recognize which foods support your well-being and which may not.
In conclusion, nutrition is a cornerstone of health that influences physical vitality, mental clarity, and disease prevention. By focusing on a balanced diet rich in whole foods and essential nutrients, you can enhance your overall health and well-being. Investing in your diet today lays the foundation for a healthier tomorrow.